Do you ever wonder how the vacuum cleaners we use today came to be? Well, let’s take a trip back in time to the 1800s when the concept of household cleanliness started to shape with the help of science and technology advancements.

In the 19th century, cleanliness became increasingly valued, and people were on the lookout for innovative and convenient ways to keep their homes tidy. This period coincided with the Industrial Revolution, a time of significant technological change. Although there were early vacuum-like devices, they were far from the efficient and convenient machines we have today.
One notable example from this period was the ‘Whirlwind,’ a metal vacuum cleaner patented by Ives W. McGaffey in 1869. This device used bellows and a hand crank to create suction, which was indeed an improvement in cleaning technology. However, it was still a manual process that required a lot of physical effort.
The late 1800s set the stage for the electric age, and it was during the early 20th century that vacuum cleaner technology made significant strides. Electric motors and more practical designs paved the way for the first commercially successful electric vacuum cleaner, invented by Hubert Cecil Booth in 1901.
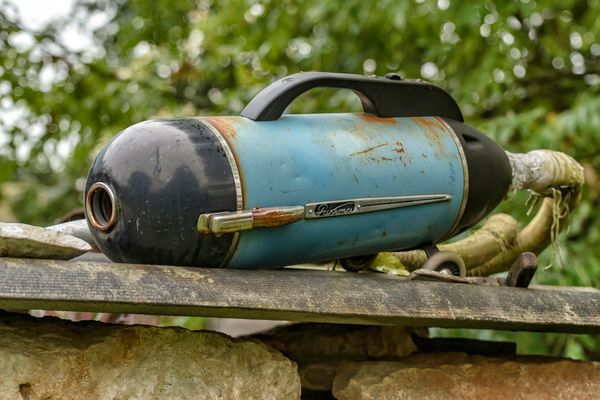

These early vacuum cleaners may seem rudimentary compared to the sleek, modern ones we have today, but they were representative of the era’s spirit of innovation. They laid the foundation for further advancements, inspiring inventors and engineers to refine and improve upon the concept.
Who would have thought that the history of vacuum cleaners could be so fascinating? It’s incredible to see how far we’ve come. So the next time you use your modern, hassle-free vacuum cleaner, take a moment to appreciate the ingenuity and progress that led us here.

Now, as you come across a vintage vacuum cleaner photo, you won’t be stumped like I was. Instead, you can appreciate the journey that vacuum cleaners have taken, from manual contraptions to the advanced, electric machines we use today.





